Investigating Solvent Effects and a Potential Application of the Wagner-Jauregg Reaction
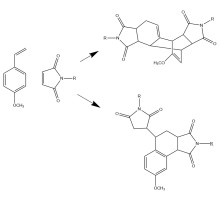
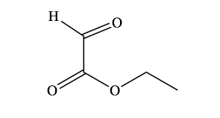
First discovered in 1930, the Wagner-Jauregg reaction consists of a Diels-Alder addition that can lead to either polymer formation or proceed through one of two possible pericyclic pathways. Specifically, it may undergo an additional Diels-Alder reaction, forming the Double-Diels-Alder product (DDA), or an ene-reaction, forming the ene-product (ene). This research investigates if solvent type plays a significant role in influencing one product over the other.