Exploring the Impacts of Functional Groups on Styrenes in the Wagner-Jauregg Reaction
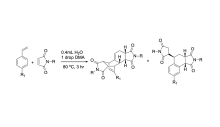
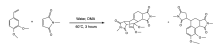
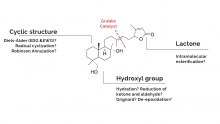
The Wagner-Jauregg reaction is a powerful, yet largely unexplored organic reaction. This reaction pathway is a specialized type of Diels-Alder reaction that facilitates the formation of large, complex ring structures. This reaction is particularly impactful in synthetic chemistry due to the use of inexpensive and readily available starting materials to create more complex molecules. The Wagner-Jauregg reaction yields two primary products: the double Diels-Alder product and the ene product.