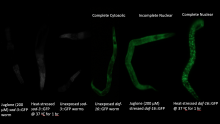
Testing the Efficacy of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles against Oxidative Stress Fluorescence Marker in C. Elegans
Characterized by a gradual disintegration of the neuronal network, neurodegeneration lies at the crossroads of numerous pathologies such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s disorders, multiple sclerosis, stroke, and others. While the cause of neurodegeneration is often multifactorial in nature (e.g., genetic, age, environmental factors), oxidative damage tends to be a common denominator in the process.